| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- stride
- linear regression
- 언리얼엔진
- ability task
- 언리얼 엔진
- gas
- UI
- 보안
- Unreal Engine
- animation
- gameplay ability system
- attribute
- Multiplay
- CTF
- 게임 개발
- 게임개발
- gameplay tag
- widget
- C++
- unity
- MAC
- os
- listen server
- Aegis
- local prediction
- gameplay effect
- Replication
- photon fusion2
- 유니티
- rpc
- Today
- Total
Replicated
Classification / 앙상블, 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝, K-fold CV, 성능 평가 본문
분류 알고리즘 타입
트리 베이스
- Decision Tree
- Random forest
- XGboost (CatBoost)
신경망 베이스
- ANN
기타
- Logistic Regression
- Naive Bayes
- KNN
- SVM
Ensemble
다수 협의에 의한 결정이라는 원리를 예측 문제 해결에 적용한 것
- 일반적으로 예측 문제에는 하나의 모델을 사용
- 여러 개의 모델을 학습시킨 뒤 그 모델들의 예측 결과들을 취합하여 최종 결정을 내린다면 예측 정확도 향상에 도움이 됨
- 결정 트리 기반 모델들에서 많이 사용
앙상블에는 크게 두 종류
- 배깅(bagging): Random Forest
- 부스팅(boosting): AdaBoost, GBM, LightGBM, XGBoost
배깅( Bootstrap Aggregation )
- 랜덤 샘플링해서 여러 모델을 만들고 여러 예측 결과를 만들어서, 결합하여 최종 결론을 내는 방법
- 주어진 데이터에서 랜덤하게 subset을 N번 샘플링해서 N개의 예측 모형을 생성
- 개별 예측 모형이 voting하는 방식으로 예측 결과를 결정하여 Low Bias는 유지하고 High Variance는 줄이는 방법
부스팅
- 예측 모델1의 결과를 보고 오답에는 가중치를 부여
- 예측 모델 2는 예측 모델 1의 오답 부분을 집중적으로 학습, 오답을 낮춤
- 예측 모델 3은 예측 모델 2의 오답 부분을 집중적으로 학습, 오답을 낮춤
- 이 과정을 반복
- 배깅에 비해 성능은 좋으나 과적합 더 쉽게 발생
Random Forest
- N개의 Decision Tree가 투표를 통해 결정
- 배깅 계열의 가장 대표적이고 예측력 좋은 알고리즘
- 예측 결과의 정확성(Low Bias)은 개별 예측 모형에 쓰이는 알고리즘의 평균값으로 유지되는 반면, 높은 분산(High Variance)은 Central Limit Theorem에 의해 낮아짐
- 회귀도 지원
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('/content/gdrive/MyDrive/Data/liver.csv')
print(df.head())
print(df.columns)
df_X = df.loc[:, df.columns != 'category']
df_y = df['category']
train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(df_X, df_y, test_size=0.3,random_state=1234)
데이터 준비
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, random_state=1234)
model.fit(train_X, train_y)
print('Train accuracy :', model.score(train_X, train_y))
print('Test accuracy :', model.score(test_X, test_y))
pred_y = model.predict(test_X)
confusion_matrix(test_y, pred_y)
트리 10개일 때
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=1234)
model.fit(train_X, train_y)
print('Train accuracy :', model.score(train_X, train_y))
print('Test accuracy :', model.score(test_X, test_y))
pred_y = model.predict(test_X)
confusion_matrix(test_y, pred_y)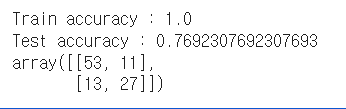
트리 50개
하이퍼 파라미터
- n_estimators : 생성하는 트리 개수, 많을수록 성능이 좋아지고 보통 500, 1000이면 충분
- max_features : 트리가 분할 시 고려할 특성의 수, 기본 오토
- max_depth : 개별 트리의 최대 깊이
- min_samples_leaf : 트리의 최하단 노드들이 가져야 할 최소 샘플 수
- Criterion : 분할 기준 측정, 기본값 gini
Hyper Paramter Tuning
- 대부분의 분류 알고리즘은 모델 성능에 영향을 끼치는 하이퍼 파라미터가 있음
- 굉장히 어렵고 많은 시간이 소요
Grid Search Cross Validation(CV)
- 지정된 하이퍼 파라미터 후보들을 모든 조합으로 시도하면서 교차 검증으로 가장 성능이 좋은 조합을 자동으로 찾아줌
비만 가능성 측정
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import pandas as pd
import pprint
import numpy as np
pp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(width=80, indent=4)
df = pd.read_csv('/content/gdrive/MyDrive/Data/PimaIndiansDiabetes.csv')
print(df.head())
print(df.columns)
df_X = df.loc[:, df.columns != 'diabetes']
df_y = df['diabetes']
base_model = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1234)
scores = cross_val_score(base_model, df_X, df_y, cv=5)
base_accuracy = np.mean(scores)
base_accuracy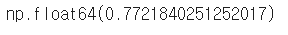
기본 성능을 교차 검증하는 예시 코드
데이터를 5등분
param_grid = {
'bootstrap': [True],
'max_depth': [80, 100],
'max_features': [2, 'sqrt'],
'min_samples_leaf': [3, 4, 5],
'min_samples_split': [8, 10, 12],
'n_estimators': [100, 200]
}
rf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1234)
grid_search = GridSearchCV(estimator = rf, param_grid = param_grid, cv = 5, n_jobs = -1, verbose = 2)
grid_search.fit(df_X, df_y)
pp.pprint(grid_search.best_params_)estimator: 분류 알고리즘
param_grid: 파라미터
cv: 모델 평가시 cv 수
n_jobs: 작업에 사용할 프로세서 수, -1은 모든 프로세서
verbose: 튜닝 과정에서 발생하는 메시지 표시 정도, 숫자가 클수록 상세정보 표시 (멀티 코어 시 사용 안함)

이런식으로 가장 적절한 파라미터를 찾아줌
best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
best_scores = cross_val_score(best_model, df_X, df_y, cv=5)
best_accuracy = np.mean(best_scores)
print('base acc: {0:0.2f}. best acc : {1:0.2f}'.format( base_accuracy, best_accuracy))
print('Improvement of {:0.2f}%.'.format( 100 * (best_accuracy - base_accuracy) / base_accuracy))
가장 좋았던 모델 들고 와서 정확도 계산
하이퍼파라미터 적용한게 더 좋음
Random Search CV
- 모든 조합을 다 시도하는 그리드 서치 대신 무작위로 샘플링한 일부 조합만 평가하는 방법
- 각 파라미터의 가능한 값 범위를 정의해두고, 그 중에서 무작위로 여러 조합을 뽑음
- 그 조합에 대해 교차 검증을 수행하여 성능을 평가하고, 가장 좋은 성능을 낸 파라미터 조합을 선택
장점
1. 예산(탐색횟수)을 유연하게 설정 가능
- 가능한 파라미터 수나 조합 수와 상관없이 몇 번만 시도하겠다는 식으로 예산을 정할 수 있음
2. 불필요한 파라미터가 있어도 효율성 유지
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pprint
pp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(width=80, indent=4)
df = pd.read_csv('/content/gdrive/MyDrive/Data/PimaIndiansDiabetes.csv')
n_estimators = [int(x) for x in np.linspace(start = 200, stop = 2000, num = 10)]
max_features = [2, 3, 5, 'sqrt']
max_depth = [int(x) for x in np.linspace(10, 110, num = 11)]
max_depth.append(None)
min_samples_split = [2, 5, 10]
min_samples_leaf = [1, 2, 4]
bootstrap = [True, False]
random_grid = {'n_estimators': n_estimators,
'max_features': max_features,
'max_depth': max_depth,
'min_samples_split': min_samples_split,
'min_samples_leaf': min_samples_leaf,
'bootstrap': bootstrap}
pp.pprint(random_grid)
rf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1234)
rf_random = RandomizedSearchCV(estimator = rf, param_distributions = random_grid, n_iter = 100, cv = 5, verbose=2, random_state=42, n_jobs = -1)n_iter : 파라미터 조합에서 선택할 조합의 수
rf_random.fit(df_X, df_y)
pp.pprint(rf_random.best_params_)
best_random_model = rf_random.best_estimator_
best_random_scores = cross_val_score(best_random_model, df_X, df_y, cv=5)
best_random_accuracy = np.mean(best_random_scores)
print('base acc: {0:0.2f}. best acc : {1:0.2f}'.format(base_accuracy, best_random_accuracy))
print('Improvement of {:0.2f}%.'.format( 100 * (best_random_accuracy - base_accuracy) / base_accuracy))그리드랑 같은 식으로 학습 및 평가 가능
하이퍼파라미터 튜닝 자동화 도구들
| 도구명 | 특징 | 지원하는 탐색 방법 |
| Optuna | - 동적 탐색 그래프를 사용하여 유연한 하이퍼파라미터 공간 탐색을 지원 - 병렬화 및 실험 이력 관리 용이 - 사용자 친화적인 API를 제공하여 쉽게 통합 가능 |
베이지안 최적화, 유전자 알고리즘, 랜덤 탐색, 그리드 탐색 |
| Ray Tune | - 대규모 병렬 처리에 특화된 분산 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝 라이브러리 - 다양한 스케줄러를 제공하여 실험을 효율적으로 관리 가능 - PyTorch, TensorFolw 등 여러 딥러닝 프레임워크와 쉽게 연동됨 |
ASHA, HyperBand. Population-Based Training(PBT), 베이지안 최적화 |
| Hyperopt | - Tree-structured Parzen Estimator(TPE) 알고리즘을 기반으로 한 베이지안 최적화 도구 - 하이퍼 파라미터 공간의 유망한 영역을 효율적 탐색 - 최적화 프로세스에 대한 시각화 기능 제공 |
TPE, 랜덤 탐색 |
| Keras Tuner | - TensorFolw 및 Keras 사용자를 위해 개발된 튜닝 라이브러리 - Keras 모델 빌더 함수와 통합되어 사용하기 쉬움 - 간단한 설정만으로 다양한 튜닝 알고리즘을 적용할 수 있음 |
HyperBand, 베이지안 최적화, 랜덤 탐색, 그리드 탐색 |
K-fold cross Validation
트레인, 테스트 데이터셋을 다르게 만들면 정확도는 달라질 것
테스트 데이터셋이 어떻게 구성되었느냐에 따라 accuracy가 원래 성능보다 높거나 낮게 나올 수 있음
-> K-fold CV
데이터셋을 K개로 나눔 (일반적으로 K는 10)
그리고 K-1개를 트레이닝에 쓰고 마지막 한 개를 테스트에 씀
모델의 정확도는 각 fold의 정확도들의 평균으로 계산
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import numpy as np
wine_X, wine_y = datasets.load_wine(return_X_y=True)
kf = KFold(n_splits=5, random_state=123, shuffle=True) # 5 fold
model = svm.SVC()
acc = np.zeros(5) # accuracy for 5 fold
i = 0
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(wine_X):
print("fold:", i)
train_X, test_X = wine_X[train_index], wine_X[test_index]
train_y, test_y = wine_y[train_index], wine_y[test_index]
model.fit(train_X, train_y)
pred_y = model.predict(test_X)
acc[i] = accuracy_score(test_y, pred_y)
print('Accuracy : {0:3f}'.format(acc[i]))
i += 1
print("5 fold :", acc)
print("mean accuracy :", np.mean(acc))
이런식으로 5개로 쪼개기 가능
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import numpy as np
wine_X, wine_y = datasets.load_wine(return_X_y=True)
model = svm.SVC()
scores = cross_val_score(model, wine_X, wine_y, cv=5, scoring='accuracy')
print("fold acc", scores)
print("mean acc", np.mean(scores))그냥 간단하게 cross_val_score 써도 됨
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
import numpy as np
wine_X, wine_y = datasets.load_wine(return_X_y=True)
model = svm.SVC()
scores = cross_validate(model, wine_X, wine_y, cv=5, scoring=['accuracy', 'balanced_accuracy'])
print("fold acc", scores)
print("mean acc", np.mean(scores['test_accuracy']))
print("mean balanced-acc", np.mean(scores['test_balanced_accuracy']))cross_validate 쓰면 여러 평가 척도 동시 적용 가능
K-fold CV의 용도
- 이게 원하는 모델을 도출해주진 않음
- 주어진 데이터셋으로 모델 개발 시 미래의 정확도를 추정
- 최종 모델 개발을 위한 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝에 사용
- 전처리 시 피쳐 셀렉션에 사용
K-fold CV로 최적의 하이퍼 파라미터 값을 확정하면 전체 데이터를 활용하여 최종 모델을 완성함
성능 지표
이진 분류 모델만을 위해
- Sensitivity (recall)
- Specificity
- precision
- F1 Score
- ROC, AUC
모든 모델을 위해
- Accuracy
이진 분류를 위한 지표..
혼동 행렬
| 실제 양성 | 실제 음성 | |
| 예측 양성 | TP | FP |
| 예측 음성 | FN | TN |
Accuracy(정확도) = (TP + TN) / (TP + FP + TN + FN)
Sensitivity(민감도, recall(재현율)) = TP / (TP + FN) .. 실제 양성 중 예측 성공
Specificity(특이도) = TN / (TN + FP) .. 실제 음성 중 예측 성공 비율
Precision(정밀도) = TP / (TP + FP) .. 양성 예측 성공률
환자(P) 정상인(N)
Sensitivity: 환자를 환자라 예측한 비율
Specificity: 정상인을 정상인이라 예측한 비율
Precision: 환자라 예측한 것에서 실제 환자의 비율
전부 값이 크면 좋음
F1 Score
- Precision과 Recall의 조화평균
- 2 * Recall * Precision / ( Recall + Precision )
- 정밀도와 재현율은 서로 트레이드 오프 관계.. 이런 불균형 반영을 위해 둘 다 높은 경우에만 높은 점수
* 다중 분류 시 Sensitivity, Specificity 이런 거 어떻게 계산하지?
각 클래스를 하나씩 기준으로 잡음(One-vs-All)
클래스 A, B, C가 있을 때
For Class A:
P: Class A
N: Class B, C
roc-auc
- roc (Receiver Operating Characteristic)
- auc (Area Under Curve)
roc 곡선
- TPR(True Positive Rate) = Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
- FPR(False Positive Rate) = FP / (FP + TN)
- ROC 곡선은 FPR을 x축, TPR을 y축으로 하여 모델의 분류 임계값을 바꾸면서 나타낸 곡선
auc
- ROC 곡선 아래 면적을 의미
- 값의 범위는 0~1
- 1.0 -> 완벽한 분류기
- 0.5 -> 랜덤 추측 수준
Accuracy는 데이터가 불균형할 때 신뢰하기 어려움
- ex. 실제 양성이 1%, 음성이 99%라면 예측을 안해도 정확도가 99%
AUC는 클래스 비율이 치우쳐 있어도 모델의 분류 능력 자체를 잘 반영함
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
test_y = [2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1]
pred_y = [0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 2]
acc = accuracy_score(test_y, pred_y)
print(acc)
정확도
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
test_y = [2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1]
pred_y = [0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 2]
confusion_matrix(test_y, pred_y)
혼동 행렬(Confusion Matrix)
test_y = [1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]
pred_y = [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]
tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix(test_y, pred_y).ravel()
(tn, fp, fn, tp)
이진 분류 시 혼동 행렬
'학부 > 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 인공신경망 개요 (0) | 2025.10.18 |
|---|---|
| Feature Selection, Model Stacking (0) | 2025.10.18 |
| Classification / 결정 트리, SVM, XGBoost (0) | 2025.10.13 |
| Regression (0) | 2025.10.12 |
| 머신 러닝 개념 (0) | 2025.10.12 |
